Researchers find potential new target for treatment of inflammatory disease
A new joint study involving researchers from Queen Mary University of London has identified potential new targets to tackle lactate-induced chronic inflammation.
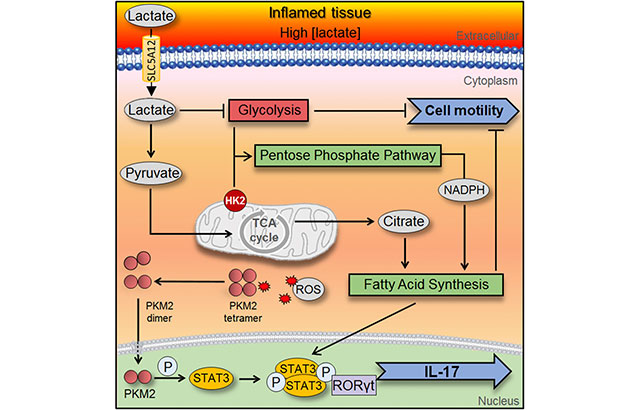
The joint study involving researchers from Queen Mary University of London was led by scientists at the University of Birmingham’s Institute of Inflammation and Ageing, Institute of Cardiovascular Sciences, and Institute of Metabolism and Systems Research.
The team of researchers are experts in cellular metabolism - the set of chemical reactions or ‘metabolic pathways’ that occur in living organisms in order to maintain life.
This study focused on the role of lactate in how the body’s immune system responds to inflammation. Lactate is a molecule produced by most tissues in the human body, with the highest production found in muscle, and levels of lactate in the blood are regulated by the kidney.
A high lactate level in the blood means that a disease or condition is causing lactate to accumulate. In general, a greater increase in lactate means a greater severity of the condition, and lactate levels are used by hospital medics as a critical way to monitor the health and likely recovery of patients in intensive care.
Dr Valentina Pucino, of the University of Birmingham, said: “The recent discovery of the fundamental role of metabolism in immune cell biology is contributing immensely to our understanding of immune cell regulation.”
Dr Michelangelo Certo, of the University of Birmingham, added: “So far, most studies have focused on the role of metabolic pathways in the establishment of the immune response.
“Lactate has mainly been seen as a by-product of metabolism or as a biomarker in critical care at best, rather than a bioactive molecule, and its functional effects have thus been neglected for a long time.
“However, far from being inert, the accumulation of lactate in the cells, molecules and structures of tissue is found in both inflammatory disease and cancer.”
In this study, the researchers analysed the response of immune cells to lactate in chronic inflammation caused by rheumatoid arthritis.
In their research, which involved the use of mice, they also used blood from healthy patients and patients with arthritis, as well as joint biopsies, and tonsils removed following tonsillectomies due to the fact that inflamed tonsils share similarities with an inflamed joint.
Dr Claudio Mauro, of the University of Birmingham’s Institute of Inflammation and Ageing, said: “We identified the pathway initiated by lactate build-up in inflamed tissue that exacerbates the inflammatory response.
“We also now can provide evidence that molecules made by immune cells to transport sodium lactate - the sodium salt of lactic acid – could be a target for treatment to stop this lactate build-up in chronic inflammatory disorders.”
The study was carried out in collaboration with Queen Mary University of London, Cancer Research UK Beatson Institute in Glasgow, the University of Glasgow, and the Università degli Studi di Milano in Italy.
The research was supported by funding from Versus Arthritis, British Heart Foundation, Queen Mary Innovation Ltd, Cancer Research UK, the Institut Pasteur Foundation Cenci-Bolognetti, the Medical Research Council, CARIPLO Foundation, and the Nuffield Foundation.
Further information
- Pucino et al (2019). ‘Lactate build-up at the site of chronic inflammation promotes disease by inducing CD4+ 1 T cell metabolic rewiring.’ Cell Metabolism.